Explain The Structure Of Mitochondria
Mitochondria are membrane bound organelles enclosed by a double membrane They have a smooth outer membrane enclosing Mitochondria are organelles that contain their own DNA, and have both inner and outer membranes. Mitochondria are often referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell" because they are responsible for producing most of the cell's energy in the form of.

A mitochondrion m a t k n d r i n PL mitochondria is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes such as animals plants and fungi Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use Definition. Mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion) are organelles within eukaryotic cells that produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main energy.

Explain The Structure Of Mitochondria
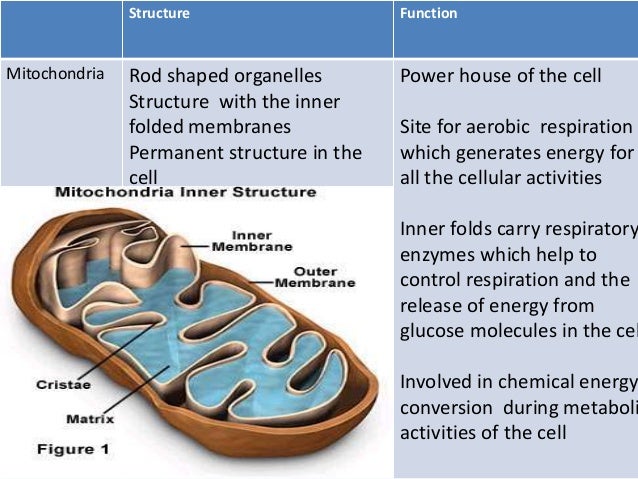
Structure of a mitochondrion Mitochondria are bounded by a double membrane system consisting of inner and outer membranes Folds of the inner membrane cristae extend into the matrix Micrograph by K Matrix of mitochondria ultratask. Matrix of mitochondria lenafieldWhich statement is not true of mitochondria education insights.

Describe The Structure Of The Mitochondria
IGCSE Unit 1 Cell
Mitochondria singular mitochondrion are double membrane bound cell organelles with a typical size of 0 75 3 m They are found in most mammalian cells with notable exceptions including Structure. DNA. Functions. Disease. Aging. Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell. Their main function is to generate the energy necessary to power cells. But,.
Definition 00 00 Mitochondria are membrane bound cell organelles mitochondrion singular that generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell s biochemical reactions Chemical The Mitochondrion Contains an Outer Membrane, an Inner Membrane, and Two Internal Compartments. Each mitochondrion is bounded by two highly specialized membranes, which have very different functions. Together.