Mean Free Path Definition
In physics mean free path is the average distance over which a moving particle such as an atom a molecule or a photon travels before substantially changing its direction or energy or in a specific context other properties typically as a result of one or more successive collisions with other particles Scattering theory Slab of target mean free path, average distance an object will move between collisions. The actual distance a particle, such as a molecule in a gas, will move before a collision, called free path, cannot generally be given because its calculation would require knowledge of the path of every particle in the region.
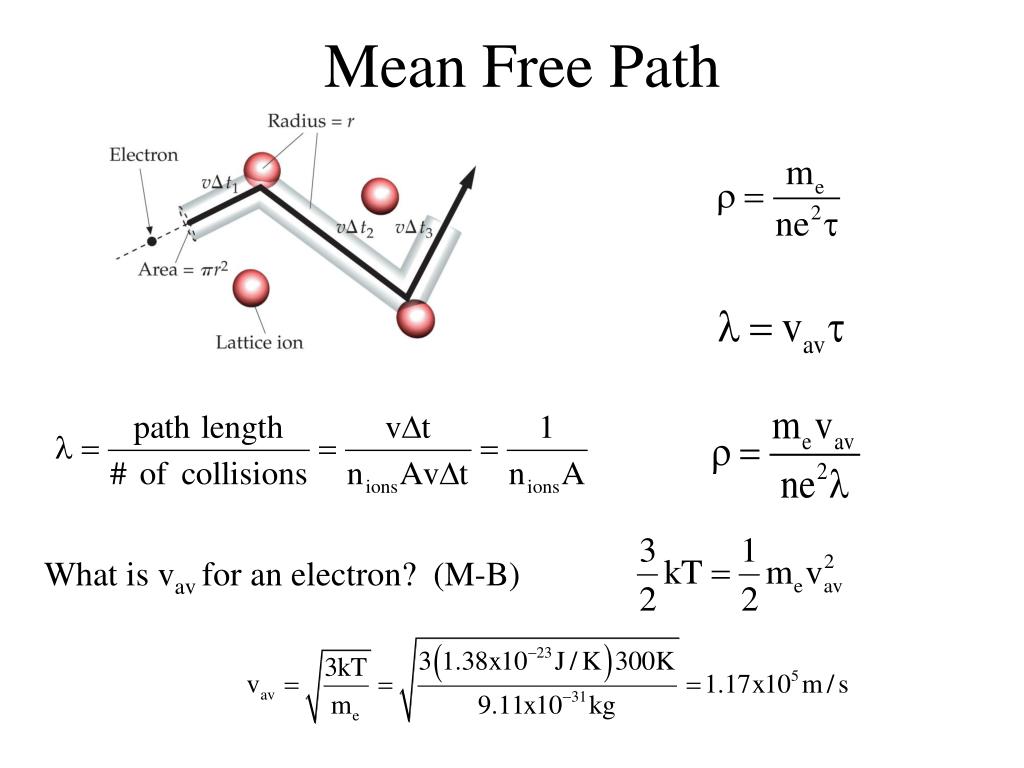
The mean free path is the average distance moved by a moving particle among successive collisions or impacts Furthermore successive collisions change the energy direction or any other particle properties of the moving particle A moving particle could also be a molecule an atom or even a photon Concept of mean free path. In a gaseous system, the molecules never move in a straight path without interruptions. This is because they collide with each other and change speed and direction. Between every two collisions, a molecule travels a path length.

Mean Free Path Definition
The mean free path is the average distance traveled by a moving particle such as an atom a molecule a photon between successive impacts collisions which modify its direction or energy or other mean free path definition formula derivation and examples. Mean free path meaning youtube mean free path definition formula derivation examples geeksforgeeks.

Mean Free Path Definition Formula Derivation And Examples
PPT Chapter 25 Current And Resistance PowerPoint Presentation Free
Merriam Webster unabridged The meaning of MEAN FREE PATH is the average distance traversed between collisions by particles such as molecules of a gas or free electrons in metal in a system of agitated particles The mean free path is the distance a particle will travel, on average, before experiencing a collision event. This is defined as the product of the average speed of a particle and the time between collisions. The former is v , while the latter is 1 / zA. Hence, we have. λ = v √2ρσ v = 1 √2ρσ.
The mean free path is defined as the distance a particle will travel on average before experiencing a collision event This is defined as the product of the speed of a particle and the time between collisions The mean free path is the average path covered by the molecules between collisions. It is known that there are different free paths with different path lengths. Given below are the free paths, λ 1 = First free path. λ 2 = Second free path. λ 3 = Third free path. λ n = nth free path.