What Is A Type 2 Error
A type II error is a statistical term used within the context of hypothesis testing that describes the error that occurs when one fails to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false A What is a Type 2 Error? A type 2 error (AKA Type II error) occurs when you fail to reject a false null hypothesis in a hypothesis test. In other words, a statistically non-significant test result indicates that a population effect does not exist when it actually does.

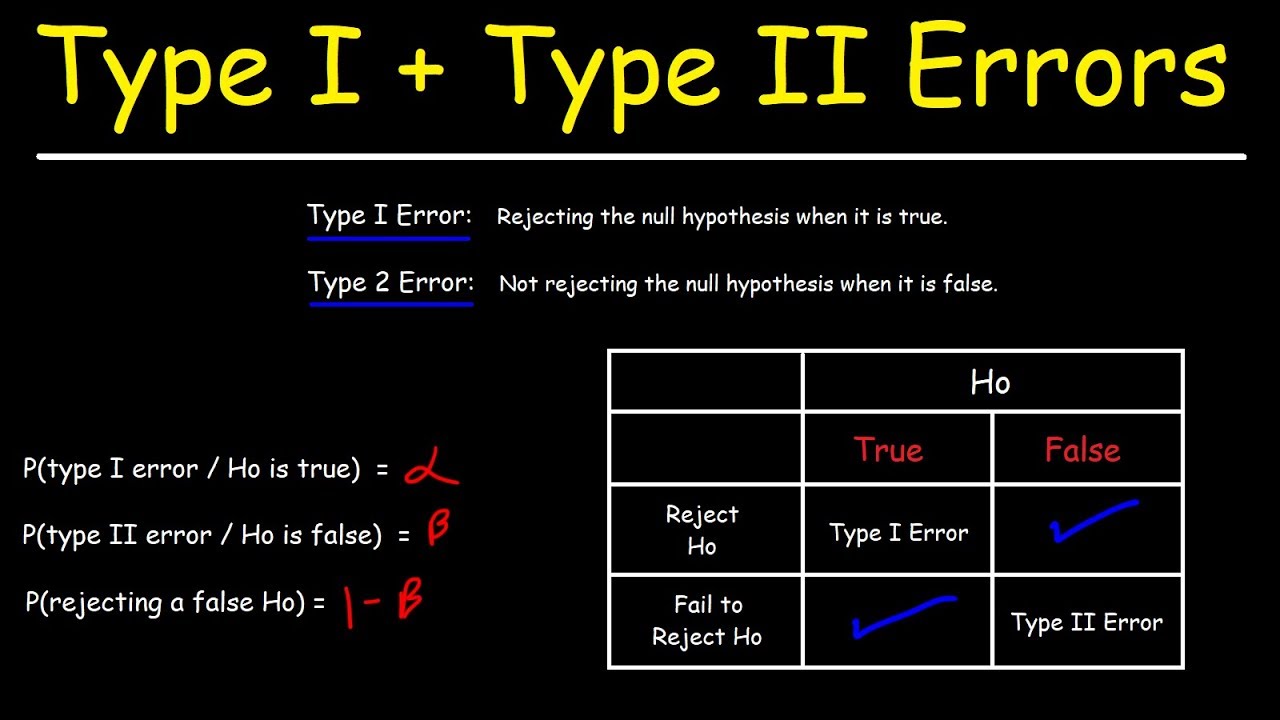
Briefly Type I errors happen when we reject a true null hypothesis Type II errors happen when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis We will explore more background behind these types of errors with the goal of understanding these statements Hypothesis Testing A type 2 error (or false negative) happens when you accept the null hypothesis when it should actually be rejected. Here, a researcher concludes there is not a significant effect when actually there really is. The probability of making a type II error is called Beta (β), which is related to the power of the statistical test (power = 1- β).
What Is A Type 2 Error
A type II error occurs when we declare no differences or associations between study groups when in fact there was 2 As with type I errors type II errors in certain cause problems Picture an example with a new less invasive surgical technique that was developed and tested in comparison to the more invasive standard care De 2626 b sta lean six sigma and statistics bilderna p pinterest. Solved 1 the probability of committing a type i error is cheggStatistics 101 calculating type ii error concept with example youtube.

Paggo Blog
What Are Type I And Type II Errors type1error type2error hypotheses
A type II error is the failure to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false A type II error is also known as a false negative finding or conclusion example a guilty person is not convicted 1 City University of New York Introductory Statistics with Probability (CUNY) 9: Hypothesis Testing for a Single Variable and Population 9.2: Type I and Type II Errors
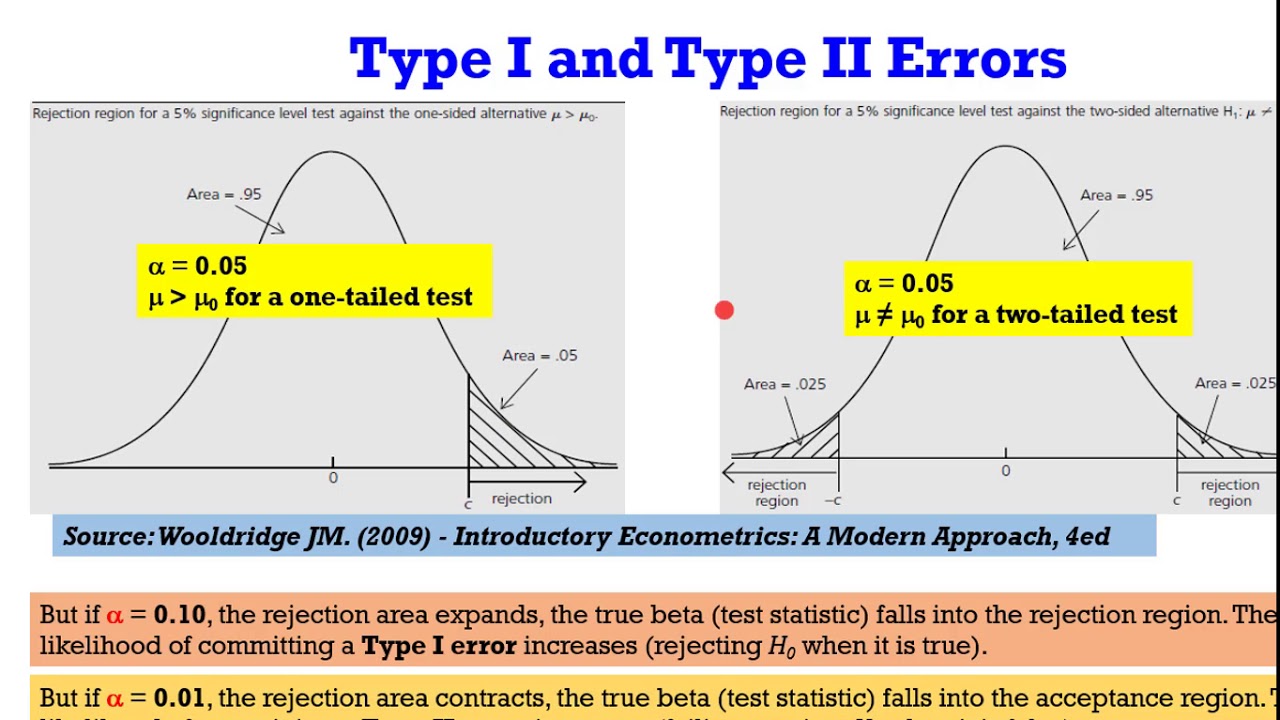
A type I Error is rejecting the null hypothesis when H 0 is actually true A type II Error is failing to reject the null hypothesis when the alternative is actually true H 0 is false We use the symbols alpha P Type I Error and P Type II Error 9.2: Outcomes, Type I and Type II Errors. When you perform a hypothesis test, there are four possible outcomes depending on the actual truth (or falseness) of the null hypothesis H0 and the decision to reject or not. The decision is not to reject H0 when H0 is true (correct decision).